Selected ATcT [1, 2] enthalpy of formation based on version 1.122g of the Thermochemical Network [3]
This version of ATcT results was generated from an expansion of version 1.122e [4] to include results centered on the determination of the appearance energy of CH3+ from CH4. [5].| Species Name | Formula | Image | ΔfH°(0 K) | ΔfH°(298.15 K) | Uncertainty | Units | Relative Molecular Mass |
ATcT ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorobenzene | C6H5F (g) | 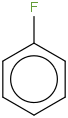 | -99.08 | -114.76 | ± 0.89 | kJ/mol | 96.1023 ± 0.0048 | 462-06-6*0 |
Representative Geometry of C6H5F (g)
Top contributors to the provenance of ΔfH° of C6H5F (g)
The 16 contributors listed below account for 91.5% of the provenance of ΔfH° of C6H5F (g).Please note: The list is limited to 20 most important contributors or, if less, a number sufficient to account for 90% of the provenance. The Reference acts as a further link to the relevant references and notes for the measurement. The Measured Quantity is normaly given in the original units; in cases where we have reinterpreted the original measurement, the listed value may differ from that given by the authors. The quoted uncertainty is the a priori uncertainty used as input when constructing the initial Thermochemical Network, and corresponds either to the value proposed by the original authors or to our estimate; if an additional multiplier is given in parentheses immediately after the prior uncertainty, it corresponds to the factor by which the prior uncertainty needed to be multiplied during the ATcT analysis in order to make that particular measurement consistent with the prevailing knowledge contained in the Thermochemical Network.
| Contribution (%) | TN ID | Reaction | Measured Quantity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49.7 | 5110.1 | C6H5F (cr,l) + 7 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + HF (aq, 60 H2O) + 2 H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -741.88 ± 0.29 kcal/mol | Good 1956 |
| 4.9 | 5111.8 | C6H5F (g) + CH4 (g) → C6H6 (g) + CH3F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 8.71 ± 0.9 kcal/mol | Ruscic W1RO |
| 4.0 | 5111.4 | C6H5F (g) + CH4 (g) → C6H6 (g) + CH3F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 8.76 ± 1.0 kcal/mol | Ruscic G4 |
| 4.0 | 5111.7 | C6H5F (g) + CH4 (g) → C6H6 (g) + CH3F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 9.08 ± 1.0 kcal/mol | Ruscic CBS-n |
| 3.3 | 5111.3 | C6H5F (g) + CH4 (g) → C6H6 (g) + CH3F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 9.37 ± 1.1 kcal/mol | Ruscic G3X |
| 2.8 | 5113.8 | C6H5F (g) + H (g) → C6H6 (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 14.42 ± 1.2 kcal/mol | Ruscic W1RO |
| 2.8 | 5112.8 | C6H5F (g) + H2 (g) → C6H6 (g) + HF (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = -18.03 ± 1.2 kcal/mol | Ruscic W1RO |
| 2.4 | 5113.7 | C6H5F (g) + H (g) → C6H6 (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 14.50 ± 1.3 kcal/mol | Ruscic CBS-n |
| 2.4 | 5113.4 | C6H5F (g) + H (g) → C6H6 (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 14.14 ± 1.3 kcal/mol | Ruscic G4 |
| 2.4 | 5112.7 | C6H5F (g) + H2 (g) → C6H6 (g) + HF (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = -17.06 ± 1.3 kcal/mol | Ruscic CBS-n |
| 2.4 | 5112.4 | C6H5F (g) + H2 (g) → C6H6 (g) + HF (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = -17.72 ± 1.3 kcal/mol | Ruscic G4 |
| 2.3 | 5111.6 | C6H5F (g) + CH4 (g) → C6H6 (g) + CH3F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 9.02 ± 1.3 kcal/mol | Ruscic CBS-n |
| 2.1 | 5113.3 | C6H5F (g) + H (g) → C6H6 (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 14.75 ± 1.4 kcal/mol | Ruscic G3X |
| 2.1 | 5112.3 | C6H5F (g) + H2 (g) → C6H6 (g) + HF (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = -16.76 ± 1.4 kcal/mol | Ruscic G3X |
| 1.8 | 5102.8 | C6H5F (g) → 6 C (g) + 5 H (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 1321.68 ± 1.50 kcal/mol | Ruscic W1RO |
| 1.6 | 5102.4 | C6H5F (g) → 6 C (g) + 5 H (g) + F (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 1319.65 ± 1.60 kcal/mol | Ruscic G4 |
Top 10 species with enthalpies of formation correlated to the ΔfH° of C6H5F (g)
The correlation coefficient is a number from -1 to 1, with 1 representing perfectly correlated species, -1 representing perfectly anti-correlated species, and 0 representing perfectly uncorrelated species.
| Correlation Coefficent (%) | Species Name | Formula | Image | ΔfH°(0 K) | ΔfH°(298.15 K) | Uncertainty | Units | Relative Molecular Mass | ATcT ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.9 | Fluorobenzene cation | [C6H5F]+ (g) | ![c1ccc(cc1)[F+]](../images/452.png) | 788.90 | 773.87 | ± 0.89 | kJ/mol | 96.1018 ± 0.0048 | 34468-25-2*0 |
| 99.9 | Fluorobenzene | C6H5F (cr,l) | 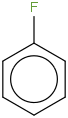 | -151.80 | -149.38 | ± 0.89 | kJ/mol | 96.1023 ± 0.0048 | 462-06-6*500 |
| 49.6 | Fluorobenzene anion | [C6H5F]- (g) | ![c1ccc(cc1)[F-]](../images/1196.png) | -18.3 | -30.2 | ± 1.8 | kJ/mol | 96.1029 ± 0.0048 | 34561-55-2*0 |
| 14.5 | Benzene | C6H6 (g) | 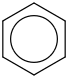 | 100.62 | 83.10 | ± 0.23 | kJ/mol | 78.1118 ± 0.0048 | 71-43-2*0 |
| 14.5 | Benzene cation | [C6H6]+ (g) | ![c1ccc(cc1)[H+]](../images/735.png) | 992.50 | 976.03 | ± 0.23 | kJ/mol | 78.1113 ± 0.0048 | 34504-50-2*0 |
| 14.5 | Benzene | C6H6 (cr,l) | 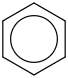 | 50.71 | 49.16 | ± 0.23 | kJ/mol | 78.1118 ± 0.0048 | 71-43-2*500 |
| 10.2 | Hydrogen fluoride | HF (aq, 60 H2O) |  | -321.17 | ± 0.16 | kJ/mol | 20.006343 ± 0.000070 | 7664-39-3*823 | |
| 10.2 | Hydrogen fluoride | HF (aq, 55.51 H2O) |  | -321.16 | ± 0.16 | kJ/mol | 20.006343 ± 0.000070 | 7664-39-3*891 | |
| 10.2 | Hydrogen fluoride | HF (aq, 50 H2O) |  | -321.15 | ± 0.16 | kJ/mol | 20.006343 ± 0.000070 | 7664-39-3*822 | |
| 10.2 | Hydrogen fluoride | HF (aq, 55 H2O) |  | -321.16 | ± 0.16 | kJ/mol | 20.006343 ± 0.000070 | 7664-39-3*905 |
Most Influential reactions involving C6H5F (g)
Please note: The list, which is based on a hat (projection) matrix analysis, is limited to no more than 20 largest influences.| 1 |
B. Ruscic, R. E. Pinzon, M. L. Morton, G. von Laszewski, S. Bittner, S. G. Nijsure, K. A. Amin, M. Minkoff, and A. F. Wagner, Introduction to Active Thermochemical Tables: Several "Key" Enthalpies of Formation Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. A 108, 9979-9997 (2004) [DOI: 10.1021/jp047912y] |
|
| 2 |
B. Ruscic, R. E. Pinzon, G. von Laszewski, D. Kodeboyina, A. Burcat, D. Leahy, D. Montoya, and A. F. Wagner, Active Thermochemical Tables: Thermochemistry for the 21st Century. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 16, 561-570 (2005) [DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/16/1/078] |
|
| 3 |
B. Ruscic and D. H. Bross, Active Thermochemical Tables (ATcT) values based on ver. 1.122g of the Thermochemical Network (2019); available at ATcT.anl.gov |
|
| 4 |
J. P. Porterfield, D. H. Bross, B. Ruscic, J. H. Thorpe, T. L. Nguyen, J. H. Baraban, J. F. Stanton, J. W. Daily, and G. B. Ellison, Thermal Decomposition of Potential Ester Biofuels, Part I: Methyl Acetate and Methyl Butanoate. J. Chem. Phys. A 121, 4658-4677 (2017) [DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b02639] (Veronica Vaida Festschrift) |
|
| 5 |
Y.-C. Chang, B. Xiong, D. H. Bross, B. Ruscic, and C. Y. Ng, A Vacuum Ultraviolet laser Pulsed Field Ionization-Photoion Study of Methane (CH4): Determination of the Appearance Energy of Methylium From Methane with Unprecedented Precision and the Resulting Impact on the Bond Dissociation Energies of CH4 and CH4+. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 9592-9605 (2017) [DOI: 10.1039/c6cp08200a] (part of 2017 PCCP Hot Articles collection) |
|
| 6 |
B. Ruscic, Uncertainty Quantification in Thermochemistry, Benchmarking Electronic Structure Computations, and Active Thermochemical Tables. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 114, 1097-1101 (2014) [DOI: 10.1002/qua.24605] |
Note that an uncertainty of ± 0.000 kJ/mol indicates that the estimated uncertainty is < ± 0.0005 kJ/mol.
The find function is based on the complete Species Dictionary entries for the appropriate version of the ATcT TN.
The molecule images are rendered by Indigo-depict.
The XYZ renderings are based on Jmol: an open-source Java viewer for chemical structures in 3D. http://www.jmol.org/.