Selected ATcT [1, 2] enthalpy of formation based on version 1.122r of the Thermochemical Network [3]
This version of ATcT results was generated from an expansion of version 1.122q [4, 5] to include a non-rigid rotor anharmonic oscillator (NRRAO) partition function for hydroxymethyl [6], as well as data on 42 additional species, some of which are related to soot formation mechanisms.| Species Name | Formula | Image | ΔfH°(0 K) | ΔfH°(298.15 K) | Uncertainty | Units | Relative Molecular Mass |
ATcT ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene cation | [C6H6]+ (g) | ![c1ccc(cc1)[H+]](../images/852.png) | 992.51 | 976.05 | ± 0.22 | kJ/mol | 78.1113 ± 0.0048 | 34504-50-2*0 |
Representative Geometry of [C6H6]+ (g)
Top contributors to the provenance of ΔfH° of [C6H6]+ (g)
The 9 contributors listed below account for 72.8% of the provenance of ΔfH° of [C6H6]+ (g).Please note: The list is limited to 20 most important contributors or, if less, a number sufficient to account for 90% of the provenance. The Reference acts as a further link to the relevant references and notes for the measurement. The Measured Quantity is normaly given in the original units; in cases where we have reinterpreted the original measurement, the listed value may differ from that given by the authors. The quoted uncertainty is the a priori uncertainty used as input when constructing the initial Thermochemical Network, and corresponds either to the value proposed by the original authors or to our estimate; if an additional multiplier is given in parentheses immediately after the prior uncertainty, it corresponds to the factor by which the prior uncertainty needed to be multiplied during the ATcT analysis in order to make that particular measurement consistent with the prevailing knowledge contained in the Thermochemical Network.
| Contribution (%) | TN ID | Reaction | Measured Quantity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18.1 | 5231.3 | C6H6 (cr,l) + 15/2 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -780.97 ± 0.09 kcal/mol | Coops 1947, Coops 1946 |
| 14.7 | 5231.1 | C6H6 (cr,l) + 15/2 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -780.98 ± 0.10 kcal/mol | Prosen 1945a, as quoted by Cox 1970 |
| 14.7 | 5231.4 | C6H6 (cr,l) + 15/2 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -780.92 ± 0.10 kcal/mol | Good 1969 |
| 10.2 | 5231.2 | C6H6 (cr,l) + 15/2 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -780.96 ± 0.12 kcal/mol | Cox 1970 |
| 4.9 | 120.2 | 1/2 O2 (g) + H2 (g) → H2O (cr,l) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -285.8261 ± 0.040 kJ/mol | Rossini 1939, Rossini 1931, Rossini 1931b, note H2Oa, Rossini 1930 |
| 4.6 | 1795.7 | C (graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -393.464 ± 0.024 kJ/mol | Hawtin 1966, note CO2e |
| 1.8 | 1795.5 | C (graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -393.468 ± 0.038 kJ/mol | Fraser 1952, note CO2f |
| 1.8 | 1795.4 | C (graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) | ΔrH°(298.15 K) = -393.462 ± 0.038 kJ/mol | Lewis 1965, note CO2d |
| 1.7 | 3340.1 | C6H6 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → CH2(CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2) (g) | ΔrH°(355. K) = -49.84 ± 0.15 (×1.542) kcal/mol | Kistiakowsky 1936 |
Top 10 species with enthalpies of formation correlated to the ΔfH° of [C6H6]+ (g)
The correlation coefficient is a number from -1 to 1, with 1 representing perfectly correlated species, -1 representing perfectly anti-correlated species, and 0 representing perfectly uncorrelated species.
| Correlation Coefficent (%) | Species Name | Formula | Image | ΔfH°(0 K) | ΔfH°(298.15 K) | Uncertainty | Units | Relative Molecular Mass | ATcT ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.9 | Benzene | C6H6 (g) | 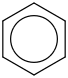 | 100.63 | 83.12 | ± 0.22 | kJ/mol | 78.1118 ± 0.0048 | 71-43-2*0 |
| 99.8 | Benzene | C6H6 (cr,l) | 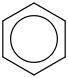 | 50.72 | 49.18 | ± 0.22 | kJ/mol | 78.1118 ± 0.0048 | 71-43-2*500 |
| 54.3 | Phenide | [C6H5]- (g) | ![c1cccc[c-]1](../images/186.png) | 244.43 | 231.01 | ± 0.38 | kJ/mol | 77.1044 ± 0.0048 | 30922-78-2*0 |
| 38.4 | Succinic acid | (CH2C(O)OH)2 (cr,l) |  | -918.56 | -940.28 | ± 0.13 | kJ/mol | 118.0880 ± 0.0034 | 110-15-6*500 |
| 37.6 | Benzoic acid | C6H5C(O)OH (cr,l) | 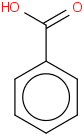 | -367.38 | -384.80 | ± 0.17 | kJ/mol | 122.1213 ± 0.0056 | 65-85-0*500 |
| 36.3 | Carbon dioxide | CO2 (g) | 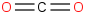 | -393.110 | -393.476 | ± 0.015 | kJ/mol | 44.00950 ± 0.00100 | 124-38-9*0 |
| 35.7 | Phenyl | C6H5 (g) | ![c1cccc[c]1](../images/78.png) | 350.67 | 337.31 | ± 0.51 | kJ/mol | 77.1039 ± 0.0048 | 2396-01-2*0 |
| 34.4 | Water | H2O (cr,l) |  | -286.298 | -285.826 | ± 0.026 | kJ/mol | 18.01528 ± 0.00033 | 7732-18-5*500 |
| 34.4 | Water | H2O (l) |  | -285.826 | ± 0.026 | kJ/mol | 18.01528 ± 0.00033 | 7732-18-5*590 | |
| 34.4 | Oxonium | [H3O]+ (aq) | ![[OH3+]](../images/1843.png) | -285.826 | ± 0.026 | kJ/mol | 19.02267 ± 0.00037 | 13968-08-6*800 |
Most Influential reactions involving [C6H6]+ (g)
Please note: The list, which is based on a hat (projection) matrix analysis, is limited to no more than 20 largest influences.| Influence Coefficient | TN ID | Reaction | Measured Quantity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.331 | 5220.6 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74555.5 ± 0.5 cm-1 | Krause 1992 |
| 0.331 | 5220.4 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74556.0 ± 0.5 cm-1 | Nemeth 1993 |
| 0.160 | 5220.2 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74555.0 ± 0.4 (×1.795) cm-1 | Chewter 1987 |
| 0.082 | 5220.5 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74556.5 ± 1.0 cm-1 | Lindner 1993, Nemeth 1993, est unc |
| 0.082 | 5220.7 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74556.3 ± 1.0 cm-1 | Goode 1997 |
| 0.030 | 5247.3 | [C6H6]+ (g) → [C6H5]+ (g) + H (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 3.90 ± 0.05 eV | Troe 2006 |
| 0.007 | 5247.1 | [C6H6]+ (g) → [C6H5]+ (g) + H (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 3.88 ± 0.10 eV | Klippenstein 1993, Klippenstein 1997, Neusser 1989 |
| 0.005 | 5220.10 | C6H6 (g) → [C6H6]+ (g) | ΔrH°(0 K) = 74553 ± 4 cm-1 | Burrill 2004, Johnson 2002a, Johnson 2002 |
| 1 |
B. Ruscic, R. E. Pinzon, M. L. Morton, G. von Laszewski, S. Bittner, S. G. Nijsure, K. A. Amin, M. Minkoff, and A. F. Wagner, Introduction to Active Thermochemical Tables: Several "Key" Enthalpies of Formation Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. A 108, 9979-9997 (2004) [DOI: 10.1021/jp047912y] |
|
| 2 |
B. Ruscic, R. E. Pinzon, G. von Laszewski, D. Kodeboyina, A. Burcat, D. Leahy, D. Montoya, and A. F. Wagner, Active Thermochemical Tables: Thermochemistry for the 21st Century. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 16, 561-570 (2005) [DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/16/1/078] |
|
| 3 |
B. Ruscic and D. H. Bross, Active Thermochemical Tables (ATcT) values based on ver. 1.122r of the Thermochemical Network, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, Illinois 2021 [DOI: 10.17038/CSE/1822363]; available at ATcT.anl.gov |
|
| 4 |
D. Feller, D. H. Bross, and B. Ruscic, Enthalpy of Formation of C2H2O4 (Oxalic Acid) from High-Level Calculations and the Active Thermochemical Tables Approach. J. Phys. Chem. A 123, 3481-3496 (2019) [DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b12329] |
|
| 5 |
B. K. Welch, R. Dawes, D. H. Bross, and B. Ruscic, An Automated Thermochemistry Protocol Based on Explicitly Correlated Coupled-Cluster Theory: The Methyl and Ethyl Peroxy Families. J. Phys. Chem. A 123, 5673-5682 (2019) [DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b12329] |
|
| 6 |
D. H. Bross, H.-G. Yu, L. B. Harding, and B. Ruscic, Active Thermochemical Tables: The Partition Function of Hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. A 123, 4212-4231 (2019) [DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.9b02295] |
|
| 7 |
B. Ruscic, Uncertainty Quantification in Thermochemistry, Benchmarking Electronic Structure Computations, and Active Thermochemical Tables. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 114, 1097-1101 (2014) [DOI: 10.1002/qua.24605] |